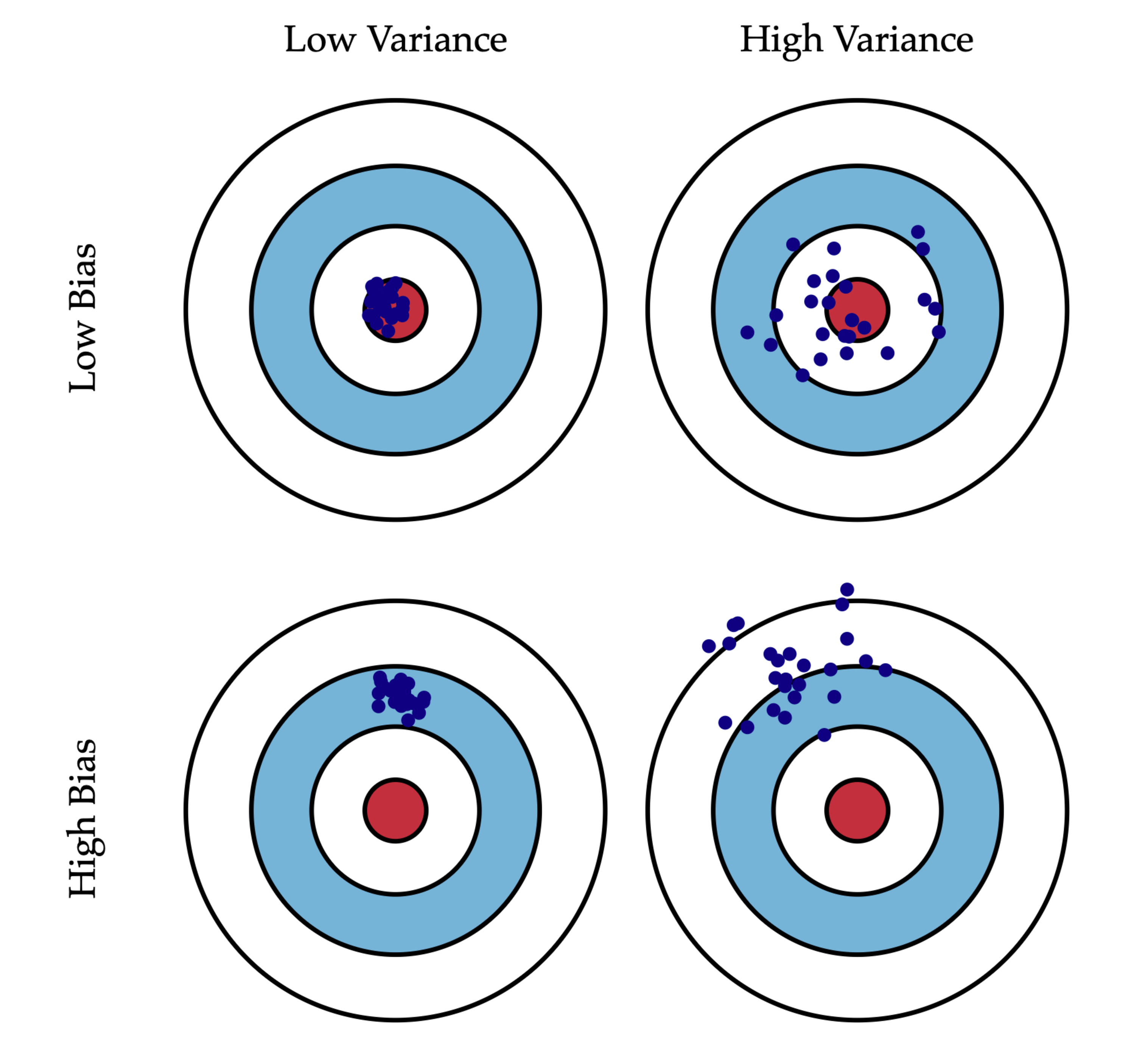
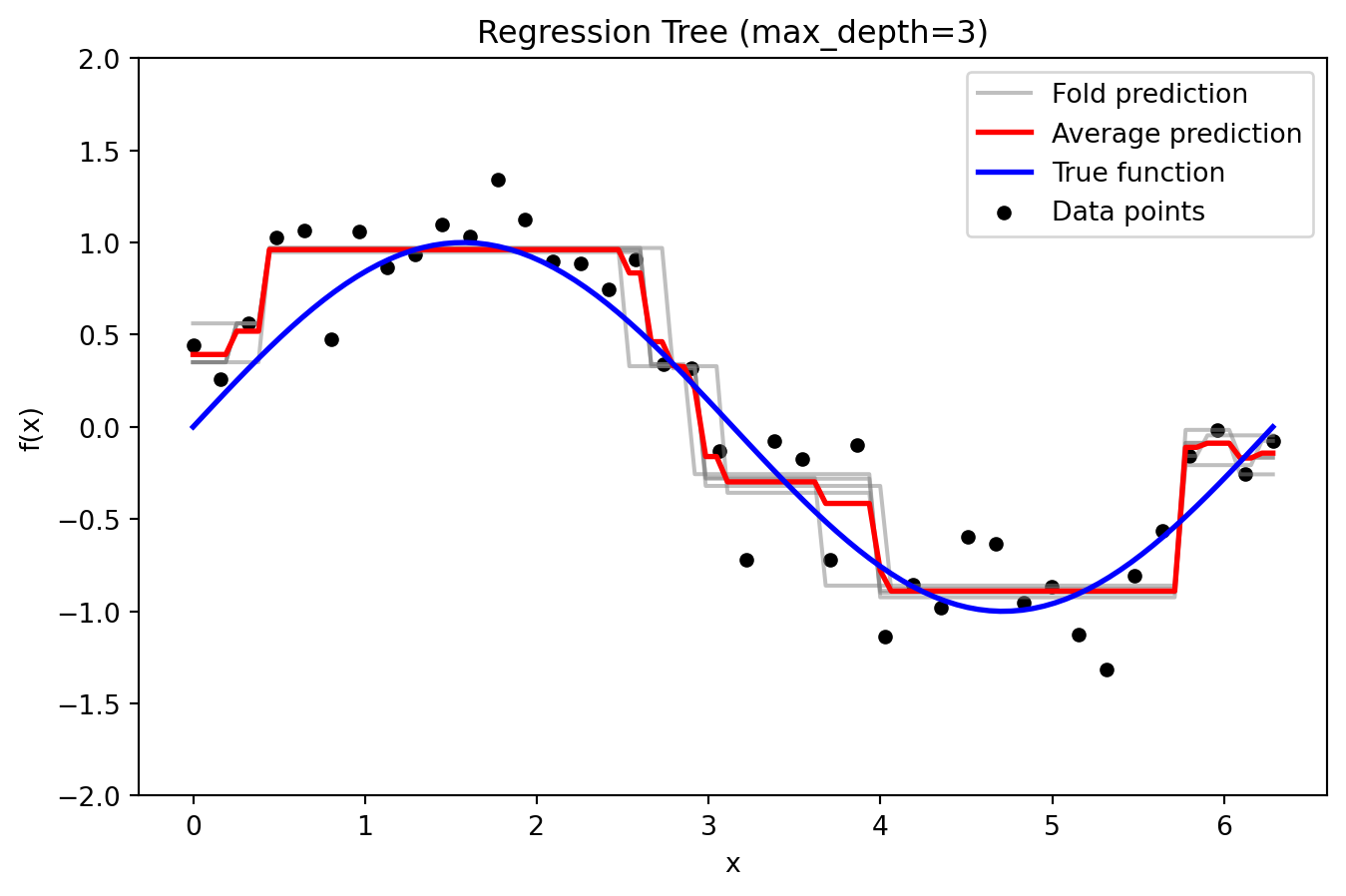
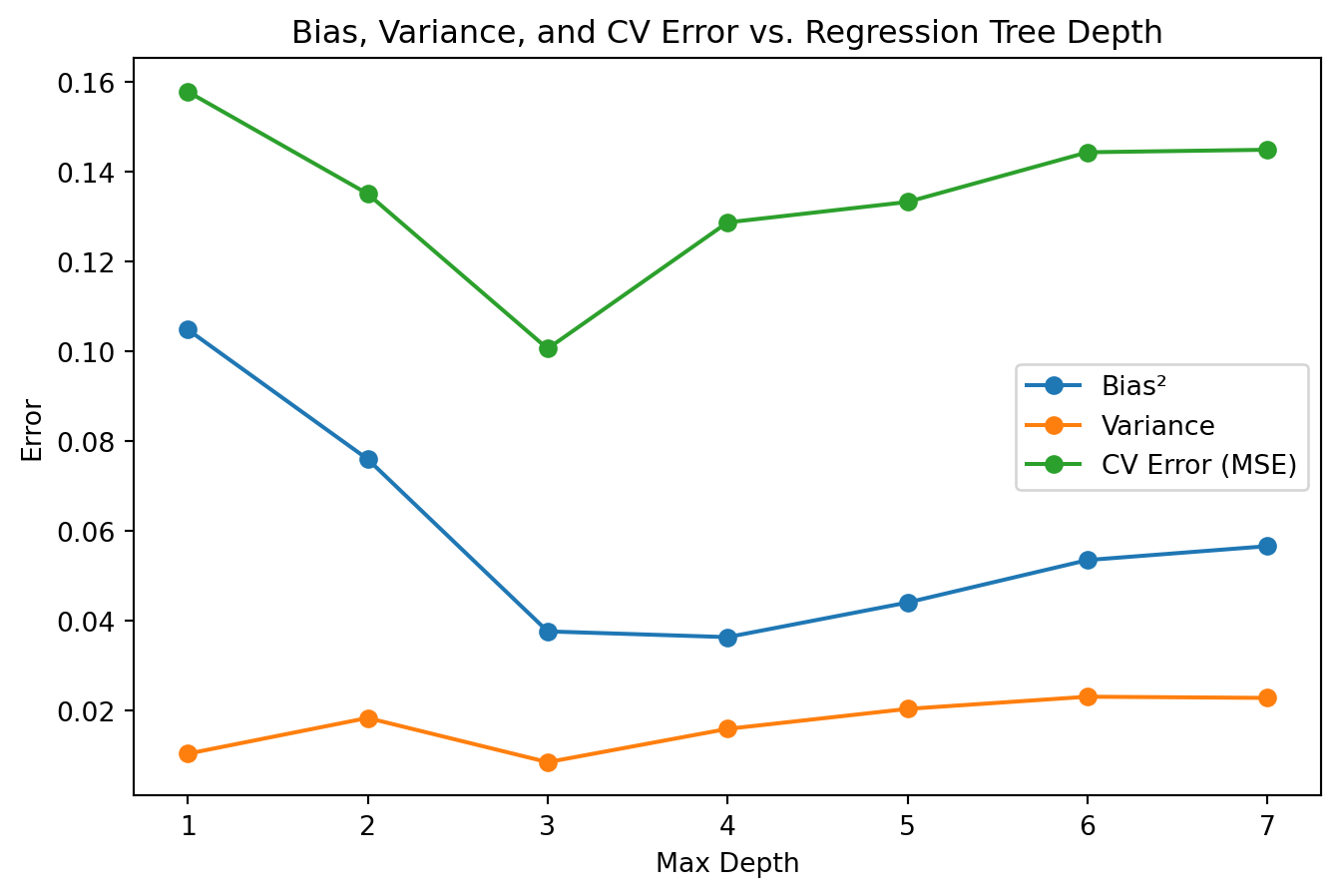
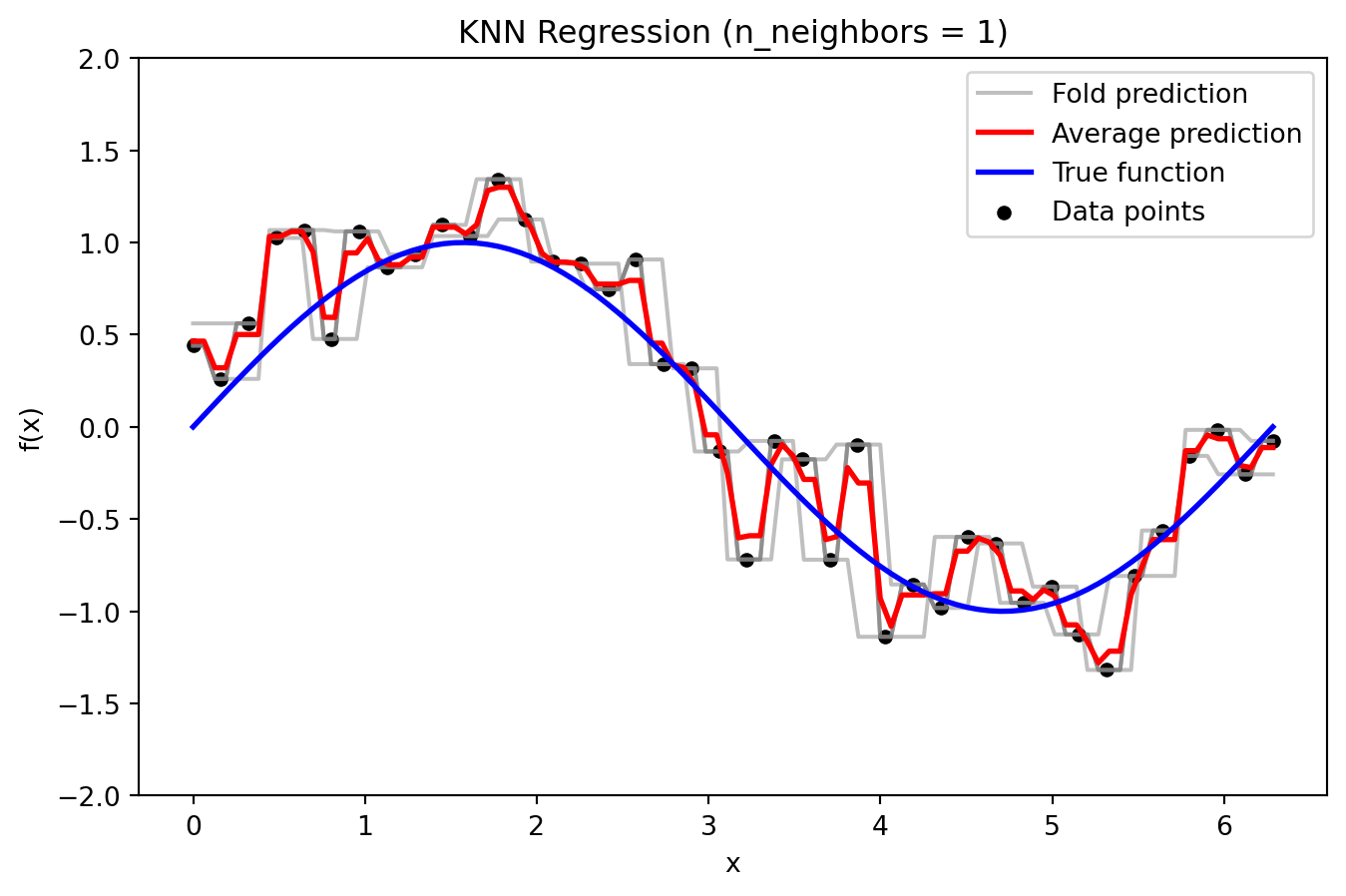
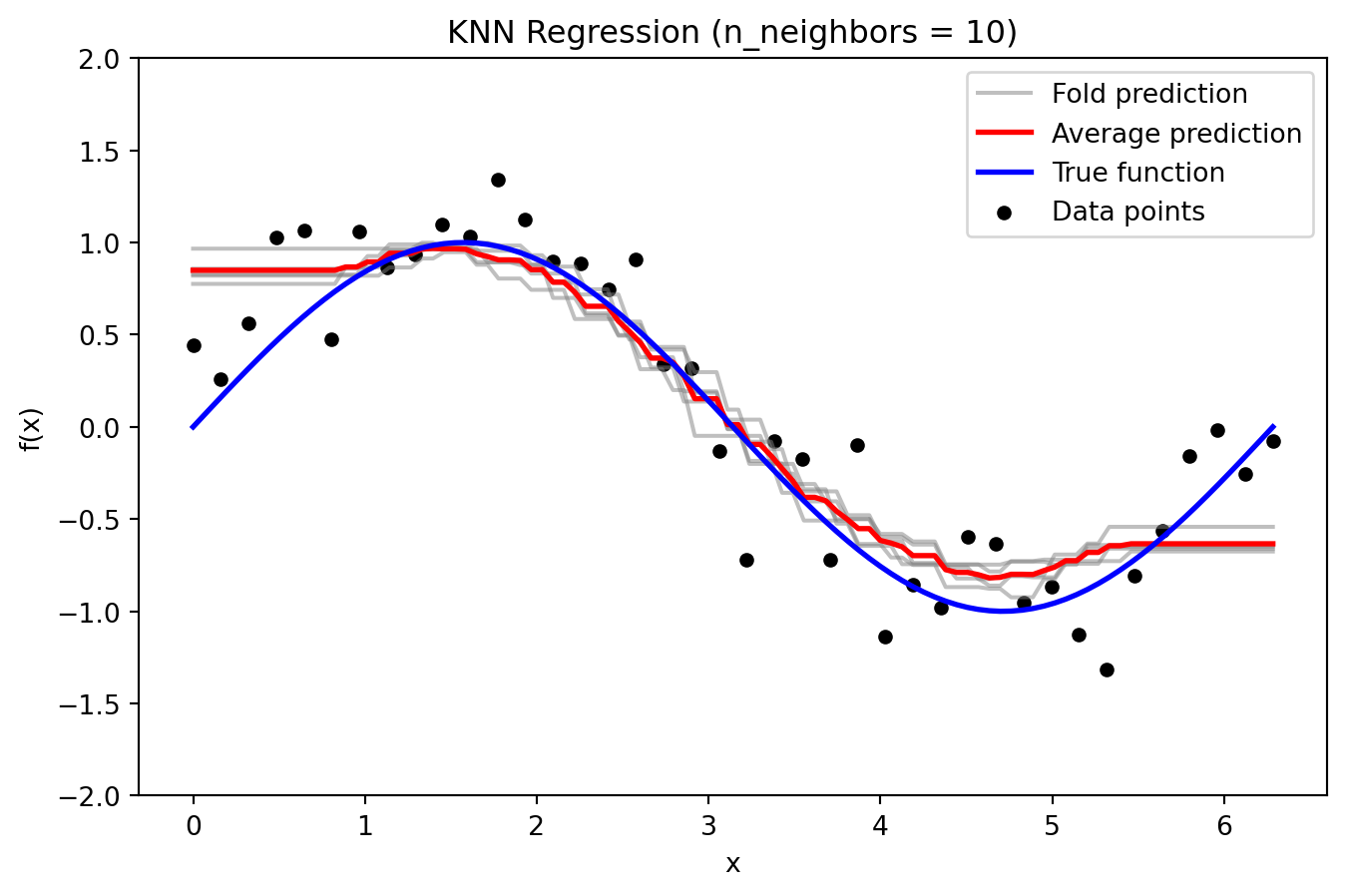
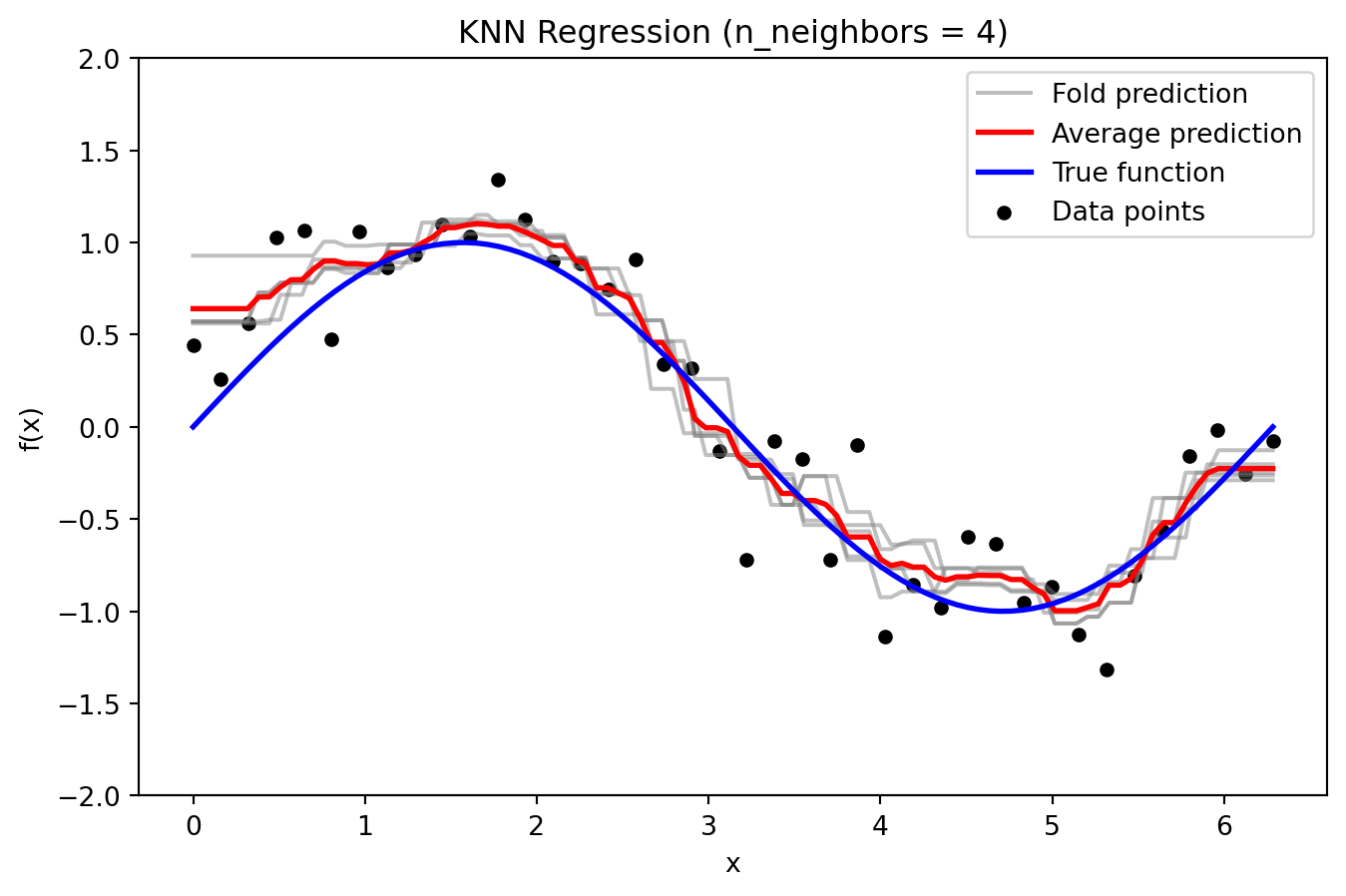
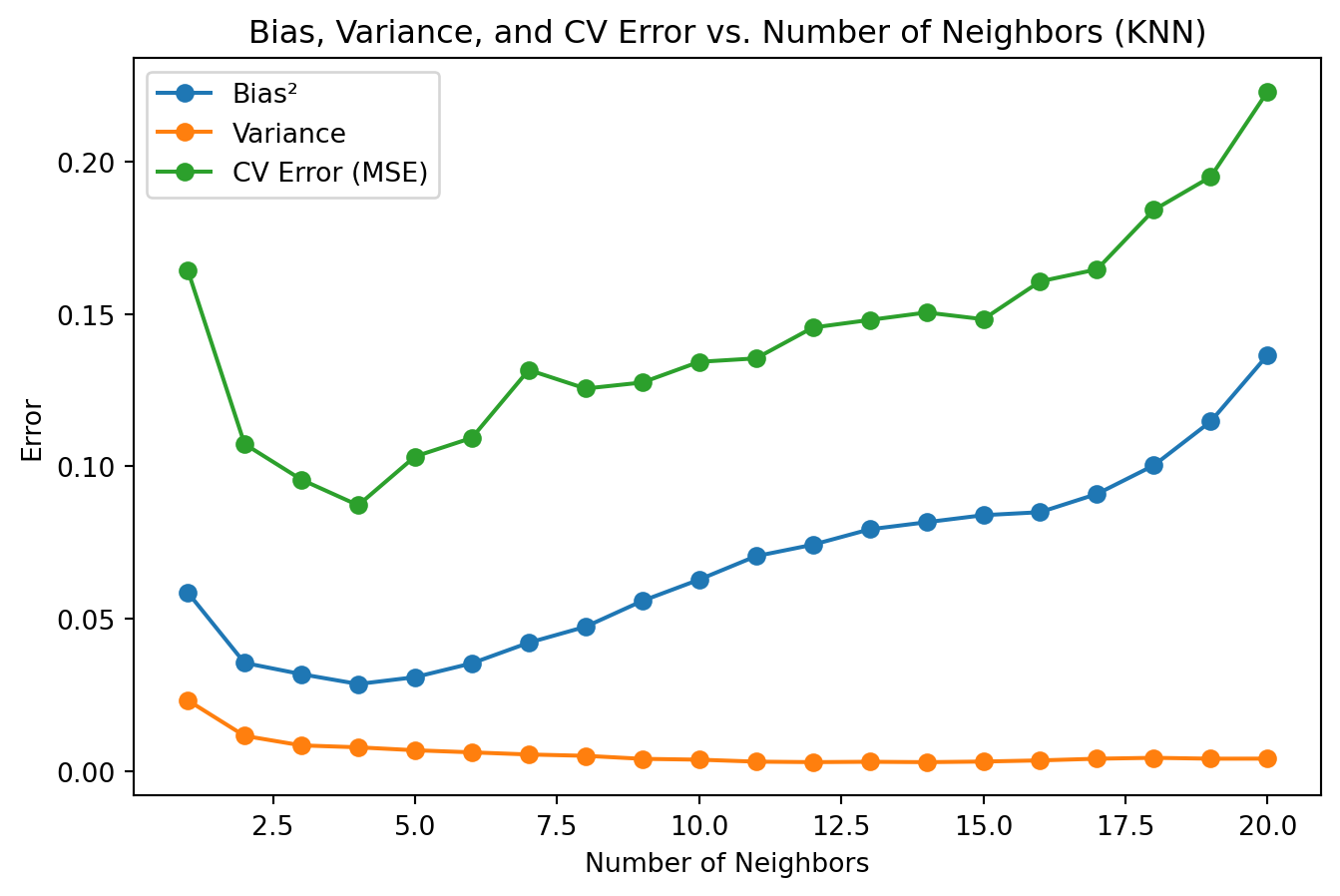
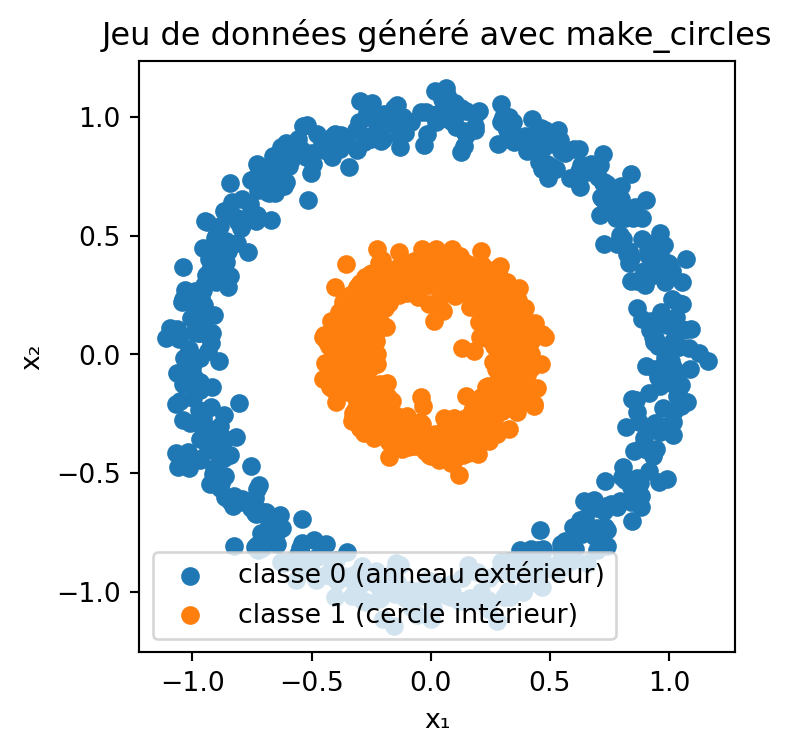
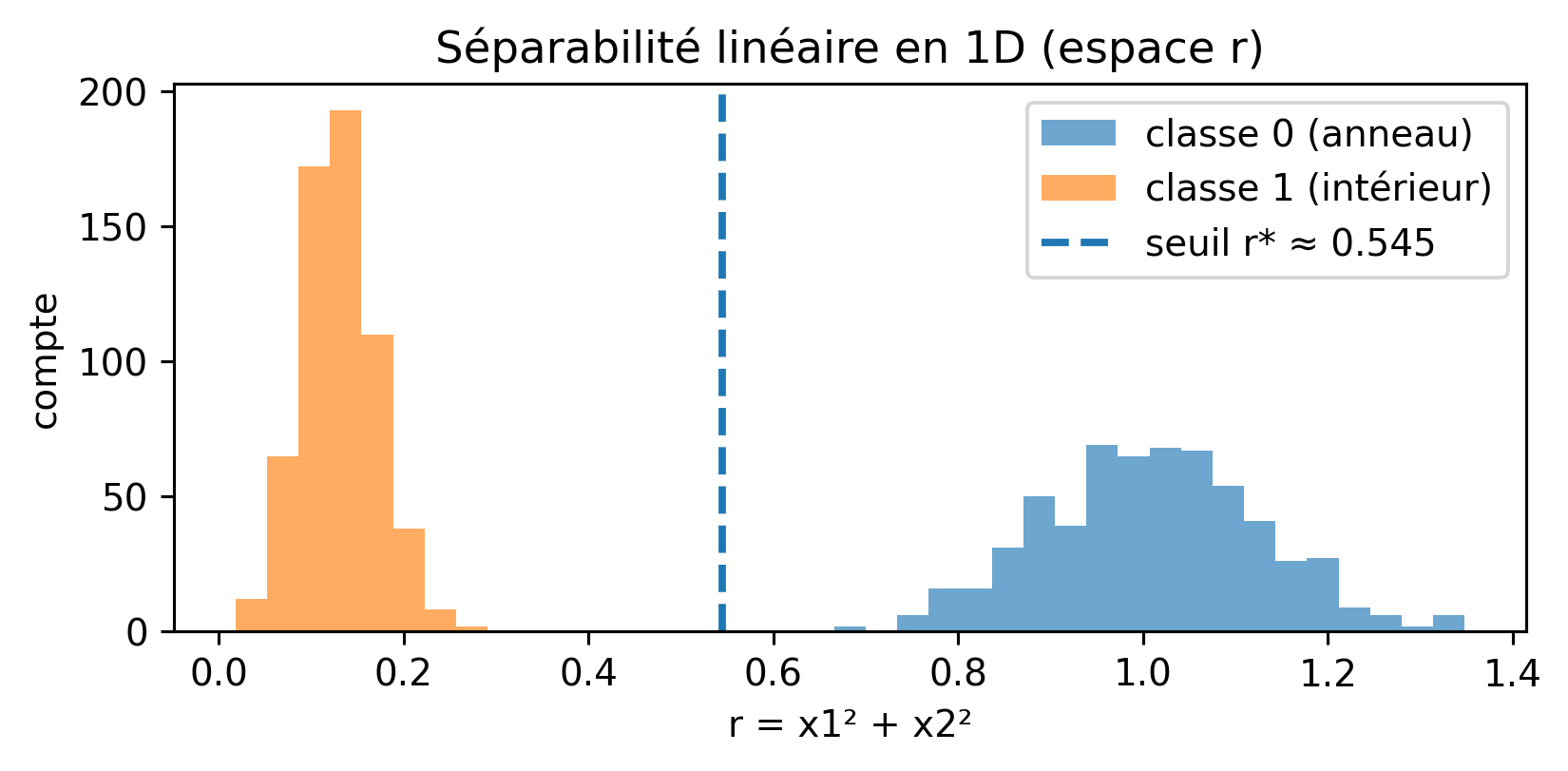
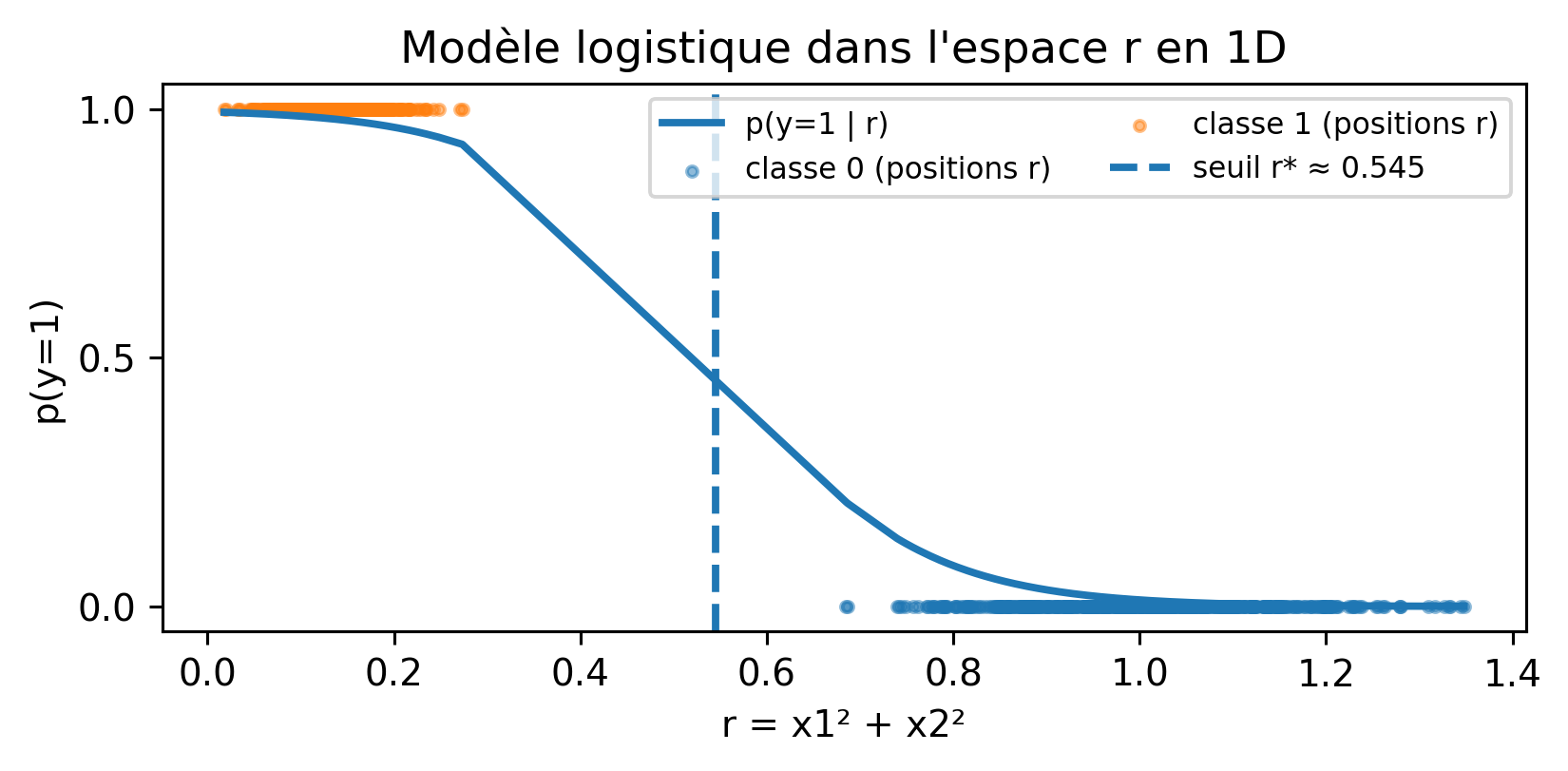
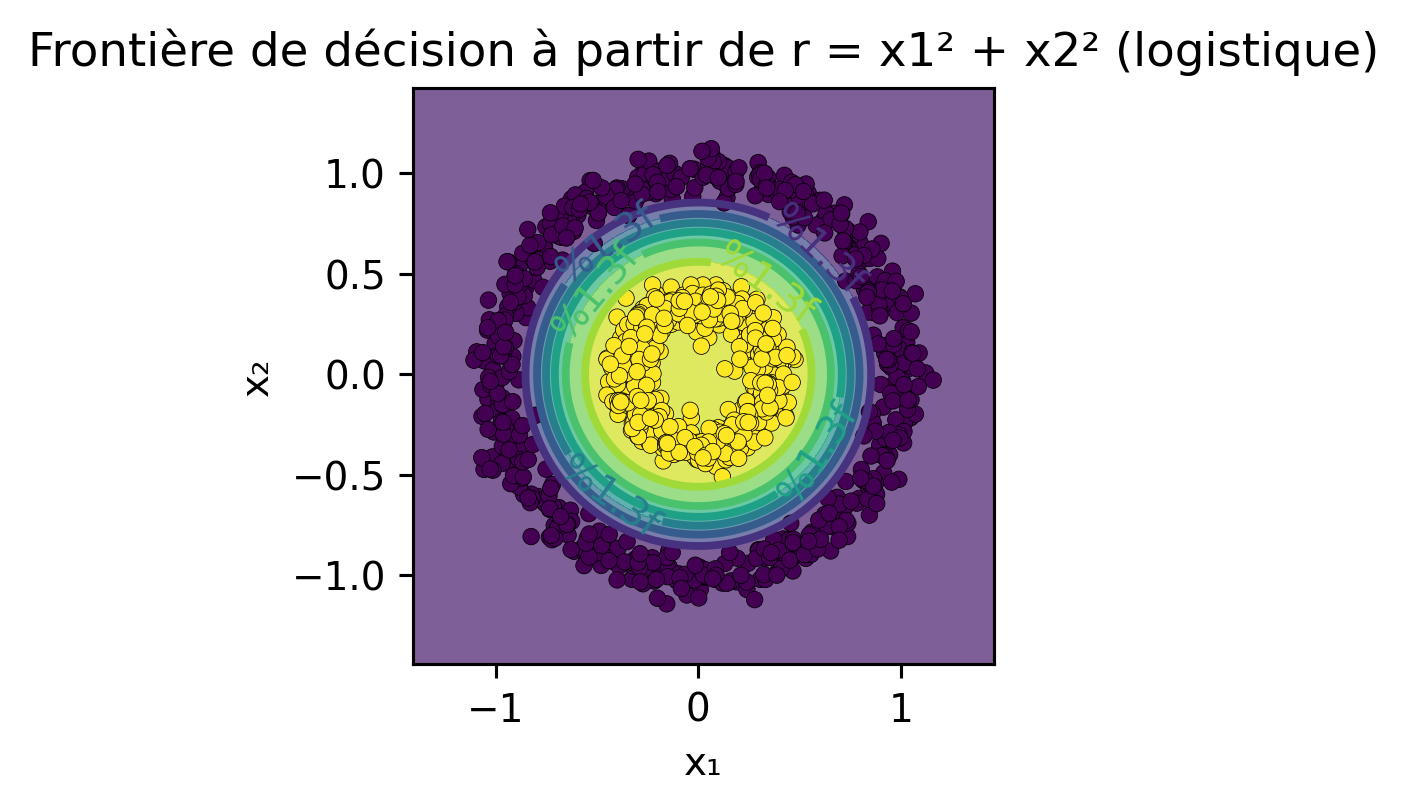
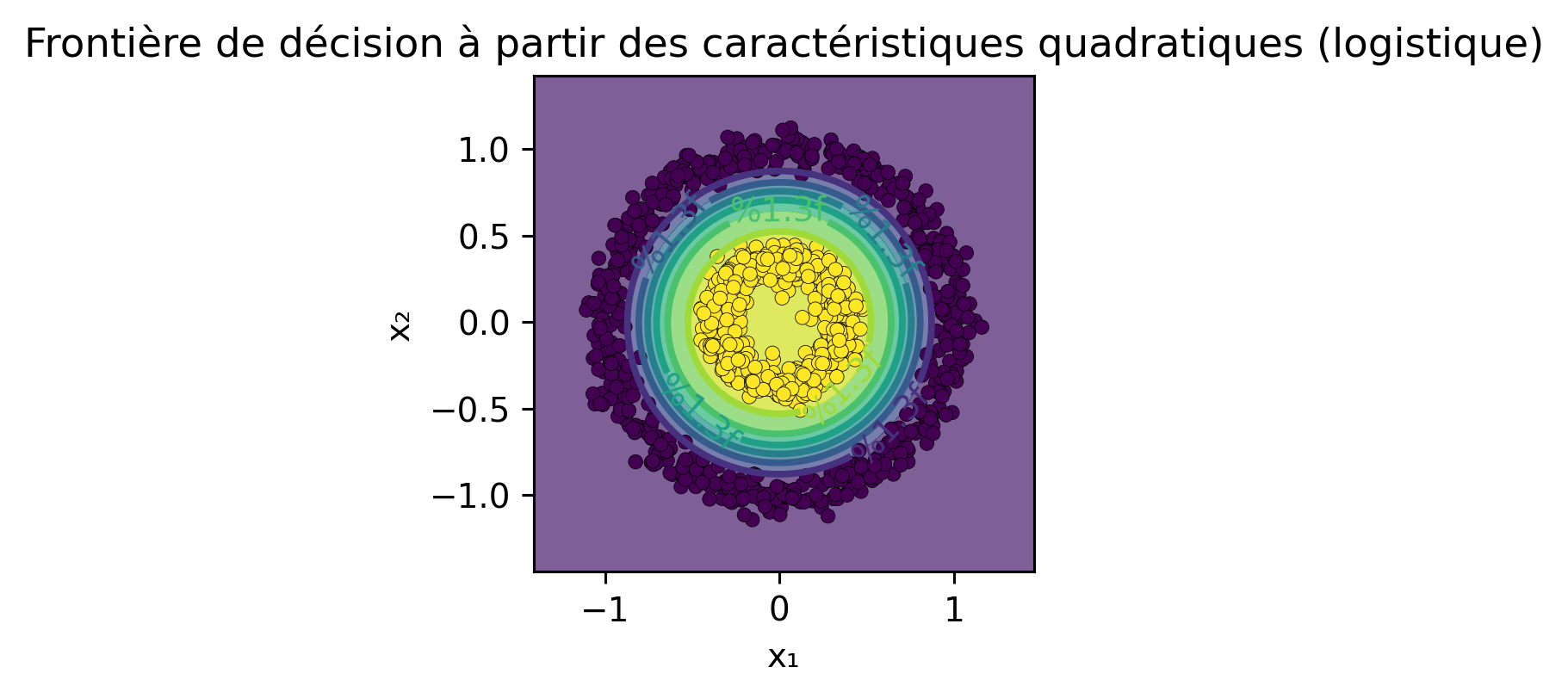
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
def true_function(x):
return np.sin(x)
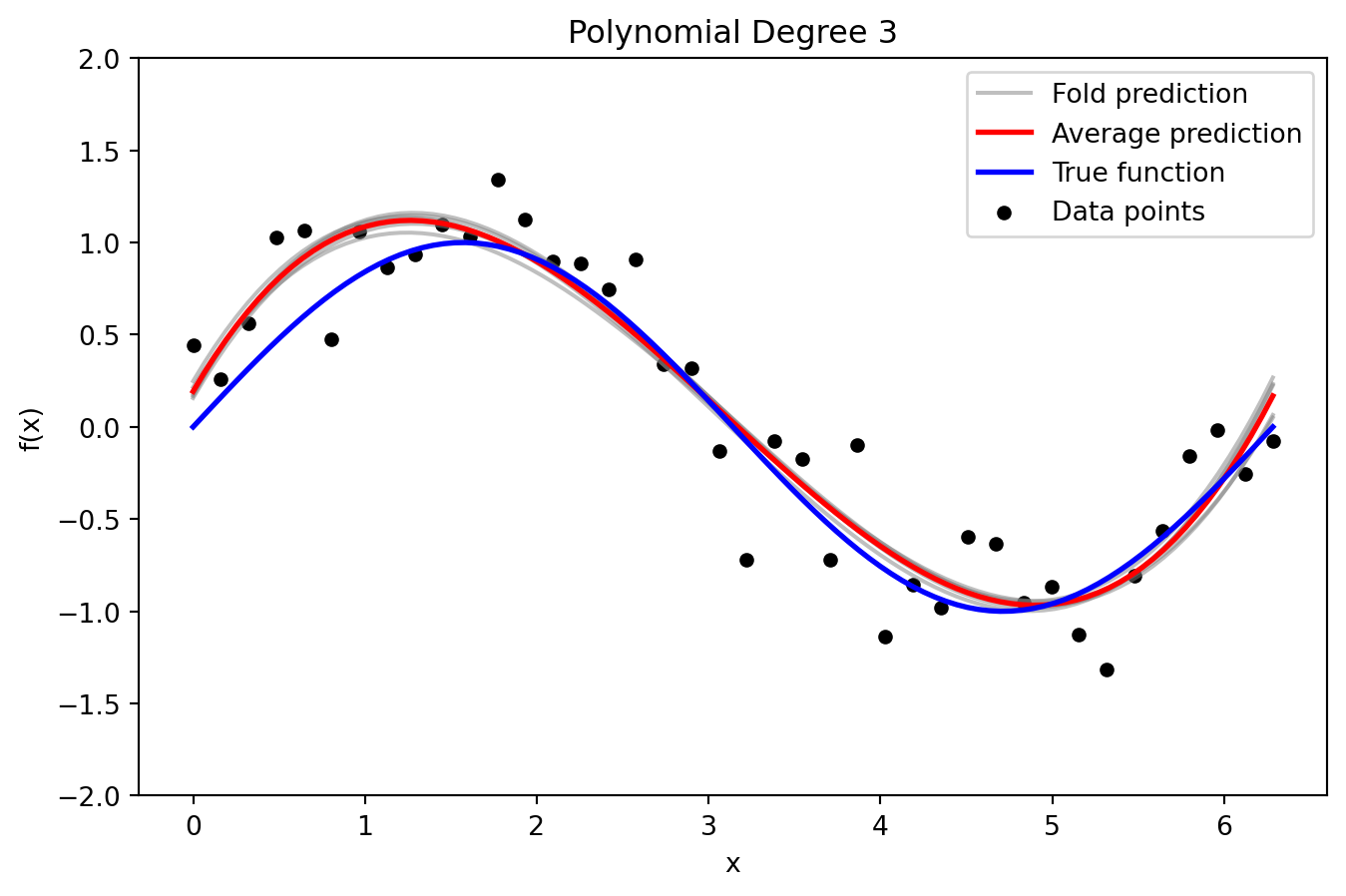
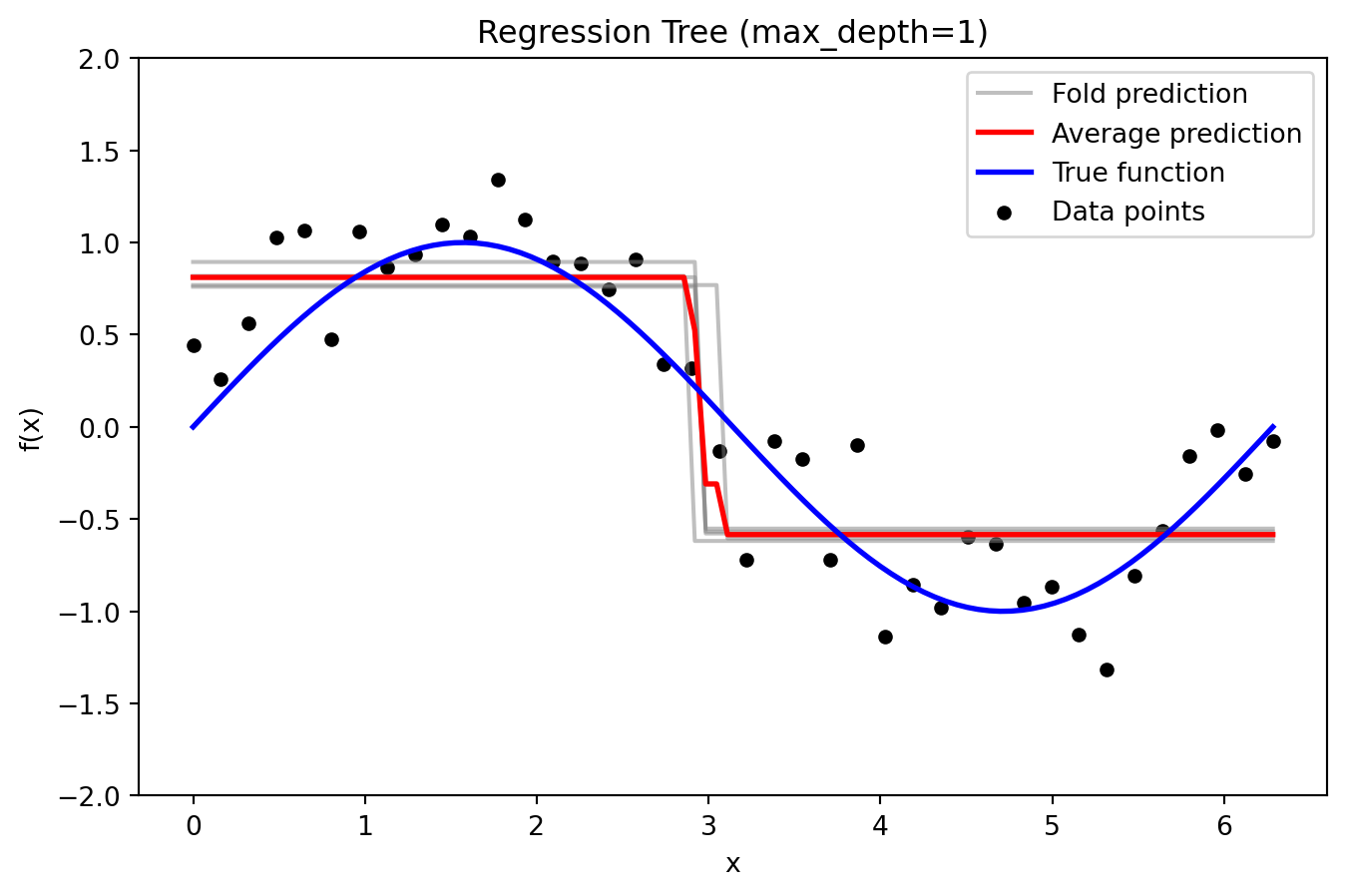
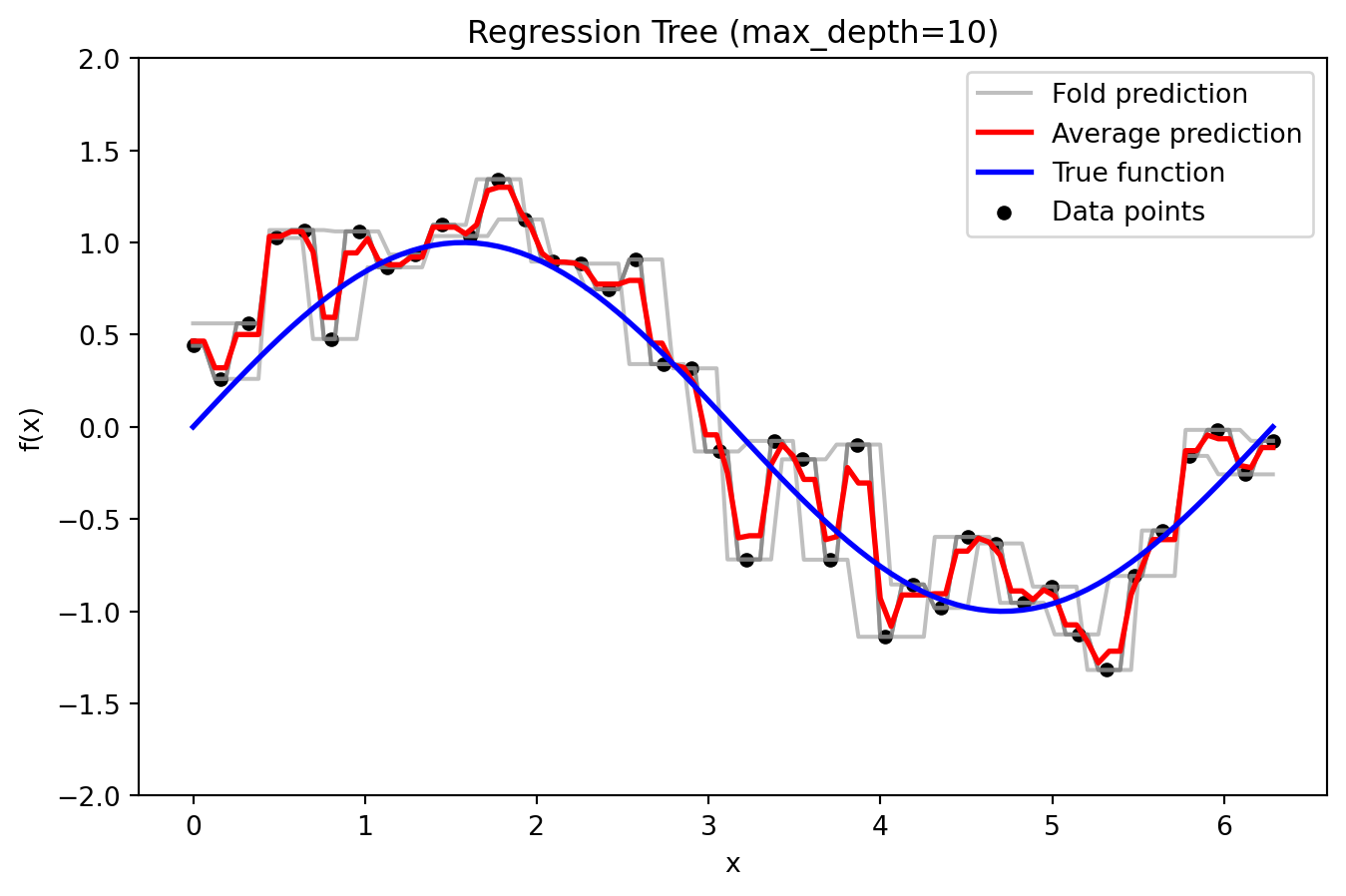
def plot_fold_predictions(degree, X, y, X_grid, y_true_grid, n_splits=5, random_state=42):
"""
For a given polynomial degree, perform KFold cross-validation,
plot the individual fold predictions along with the average prediction
and the true function (with y-axis limited to [-2, 2]),
and return predictions and errors.
"""
kf = KFold(n_splits=n_splits, shuffle=True, random_state=random_state)
fold_predictions = [] # To store predictions on the evaluation grid for each fold
fold_errors = [] # To store test errors for each fold
for train_index, test_index in kf.split(X):
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree=degree)
X_train_poly = poly.fit_transform(X[train_index])
X_test_poly = poly.transform(X[test_index])
X_grid_poly = poly.transform(X_grid)
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train_poly, y[train_index])
# Predictions on the dense grid for bias-variance analysis
y_pred_grid = model.predict(X_grid_poly)
fold_predictions.append(y_pred_grid)
# Test error on held-out data
y_pred_test = model.predict(X_test_poly)
fold_errors.append(mean_squared_error(y[test_index], y_pred_test))
fold_predictions = np.array(fold_predictions)
avg_prediction = np.mean(fold_predictions, axis=0)
# Plot individual fold predictions with y-axis limited to [-2, 2]
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))
for i in range(n_splits):
plt.plot(X_grid, fold_predictions[i], color='gray', alpha=0.5,
label='Fold prediction' if i == 0 else "")
plt.plot(X_grid, avg_prediction, color='red', linewidth=2, label='Average prediction')
plt.plot(X_grid, y_true_grid, color='blue', linewidth=2, label='True function')
plt.scatter(X, y, color='black', s=20, label='Data points')
plt.ylim(-2, 2)
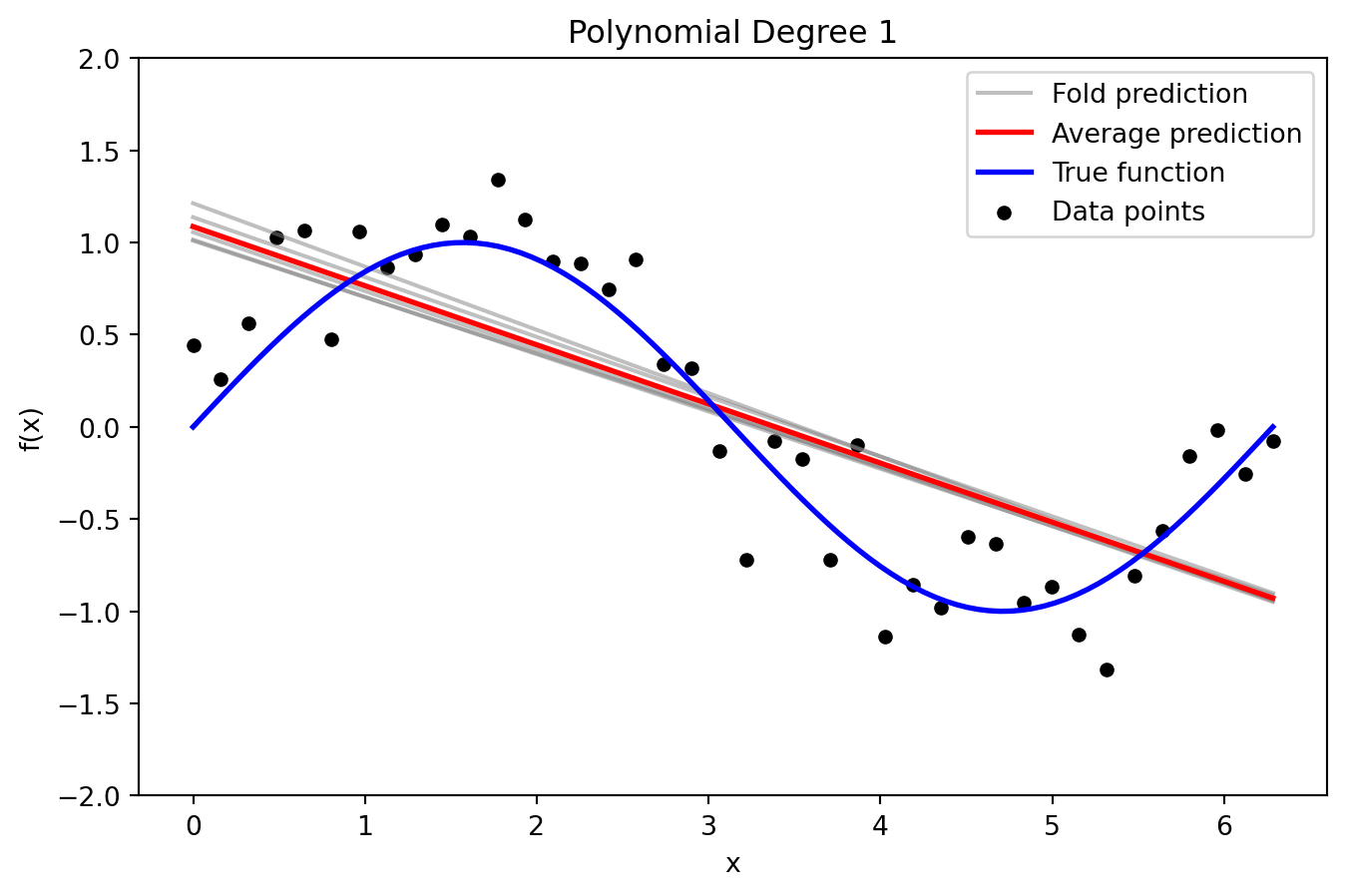
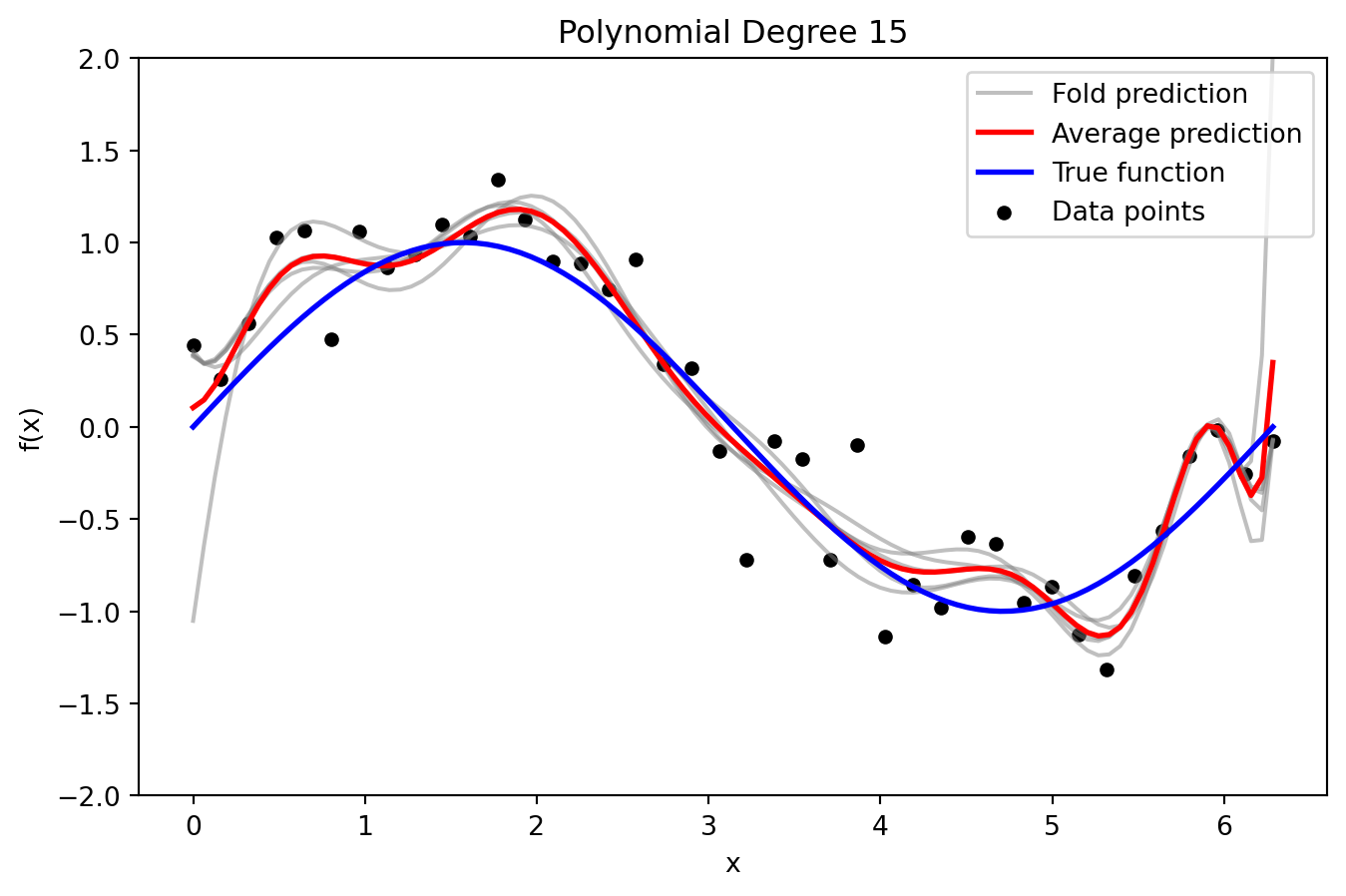
plt.title(f'Polynomial Degree {degree}')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('f(x)')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
return fold_predictions, avg_prediction, fold_errors
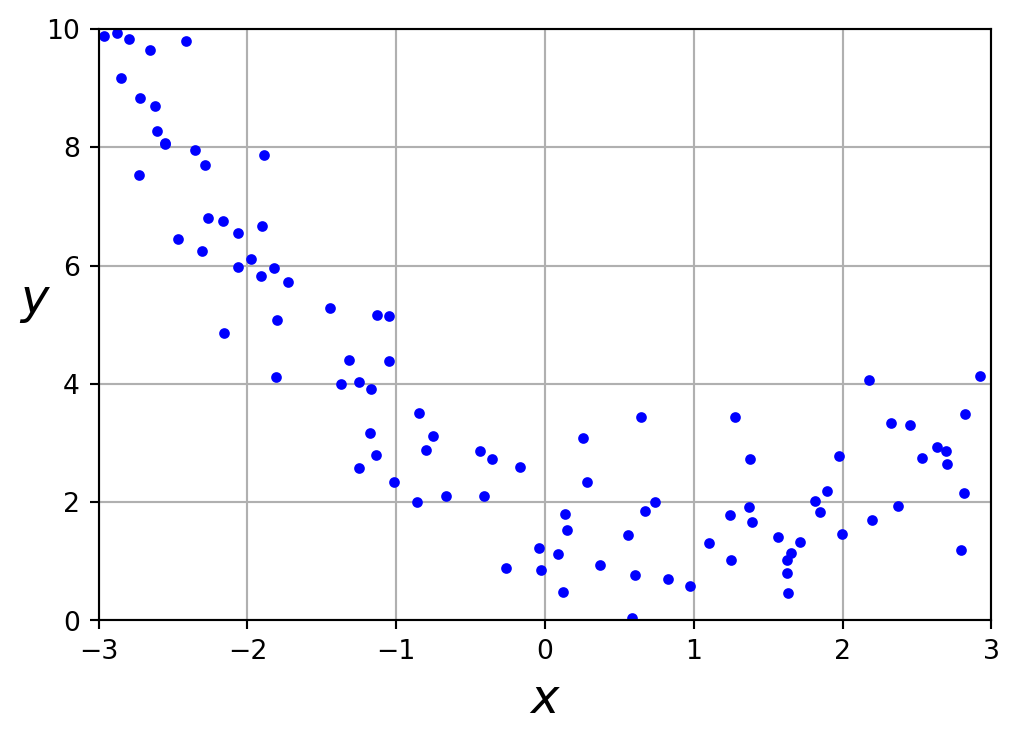
# --- Data Generation with Increased Noise and Reduced Sample Size ---
np.random.seed(0)
n_samples = 40 # Reduced sample size increases model sensitivity to training data
X = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, n_samples).reshape(-1, 1)
noise_std = 0.25 # Increased noise level amplifies prediction variability
y = true_function(X).ravel() + np.random.normal(0, noise_std, size=n_samples)
# Create a dense evaluation grid and compute the true function values
X_grid = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 100).reshape(-1, 1)
y_true_grid = true_function(X_grid).ravel()
# --- Plot Individual Fold Predictions for Selected Degrees ---
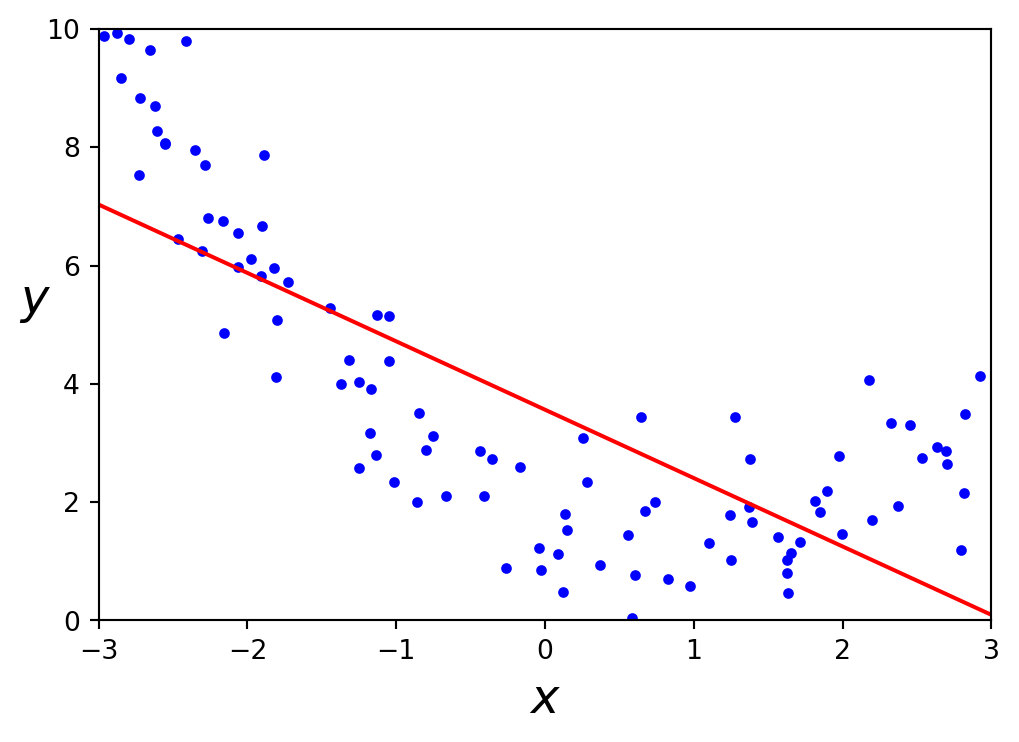
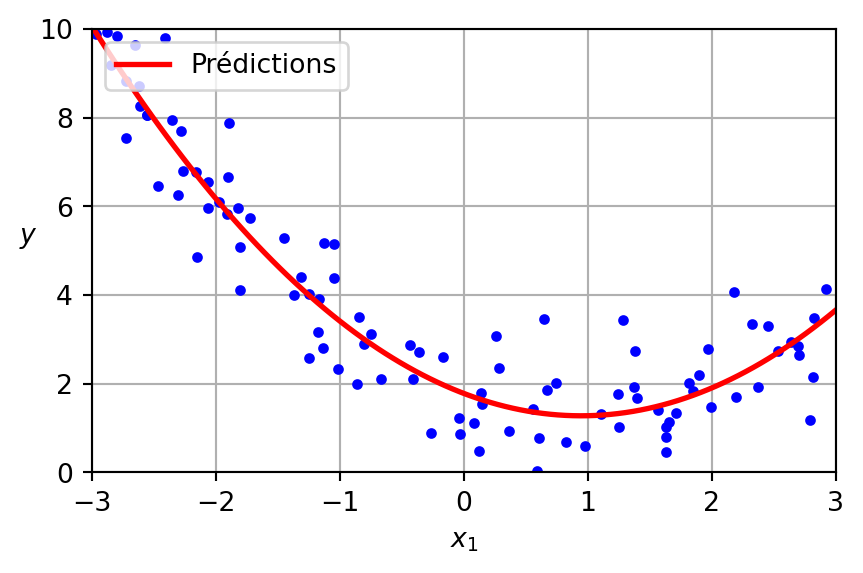
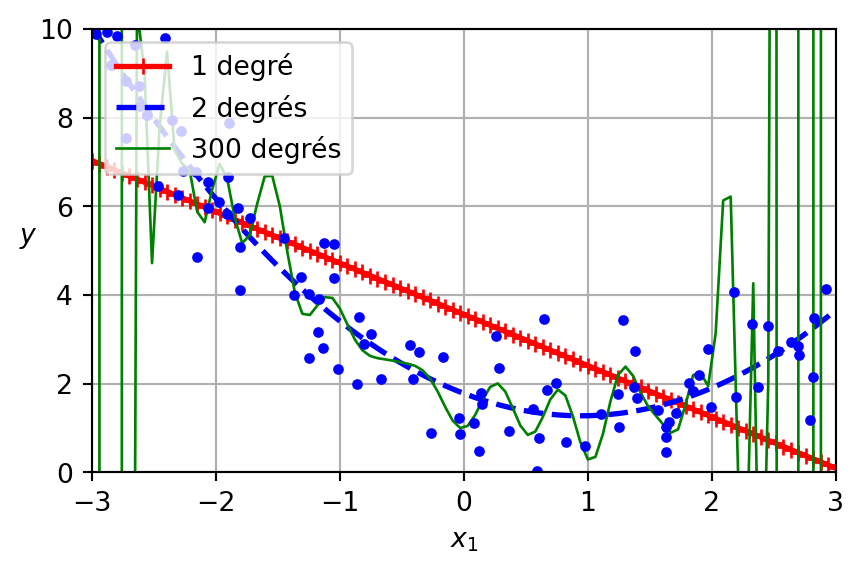
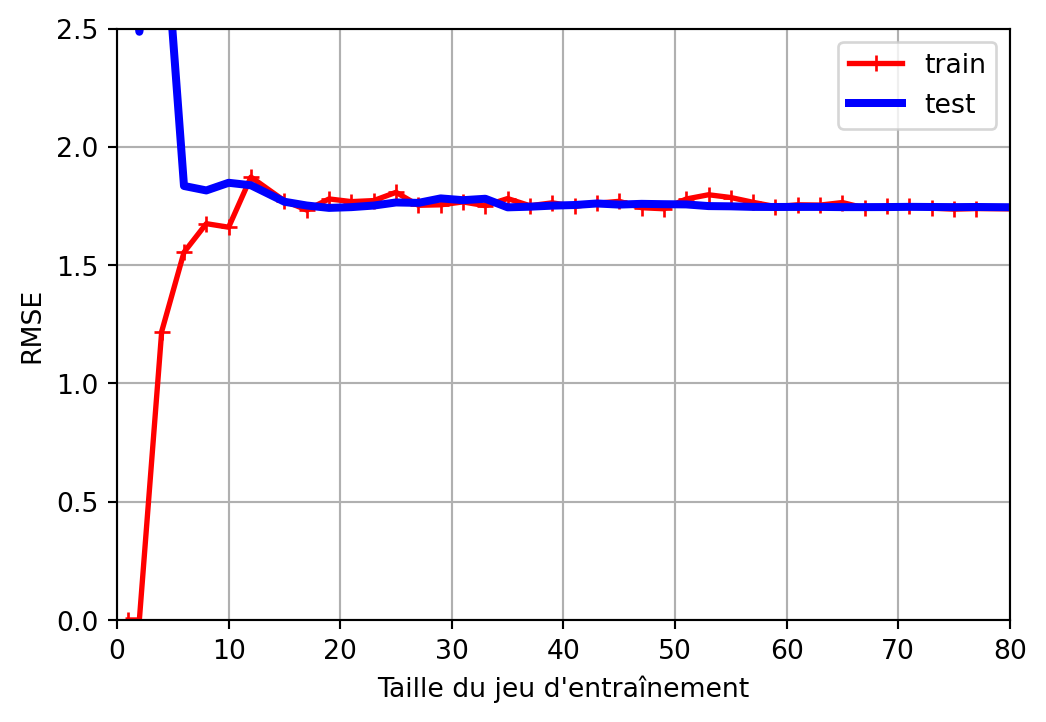
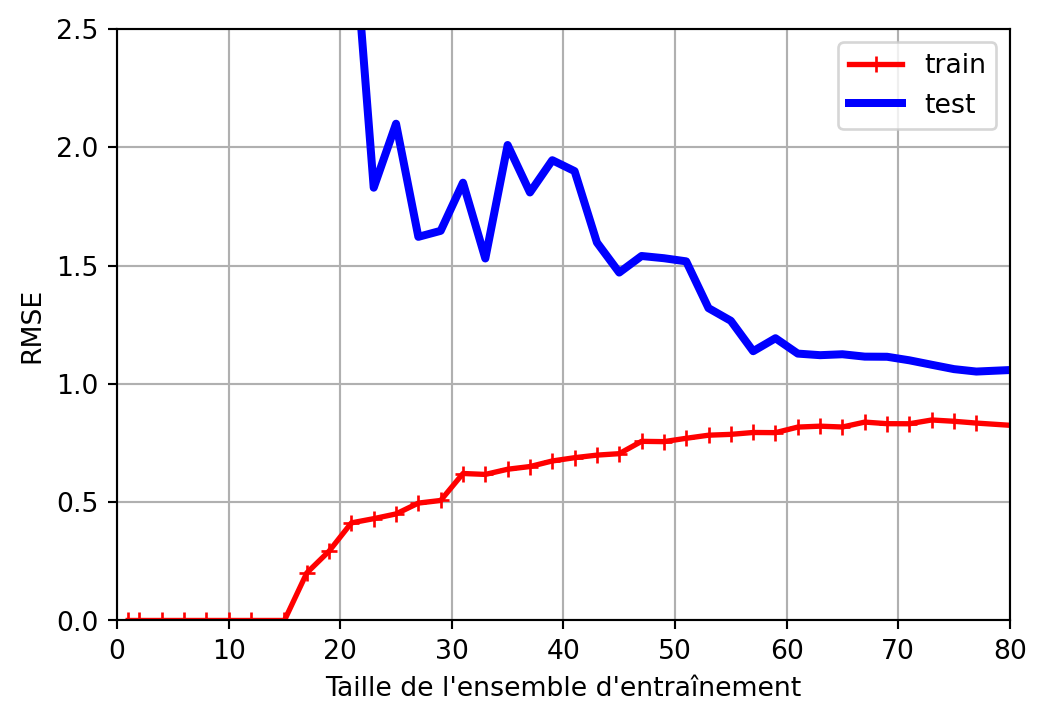
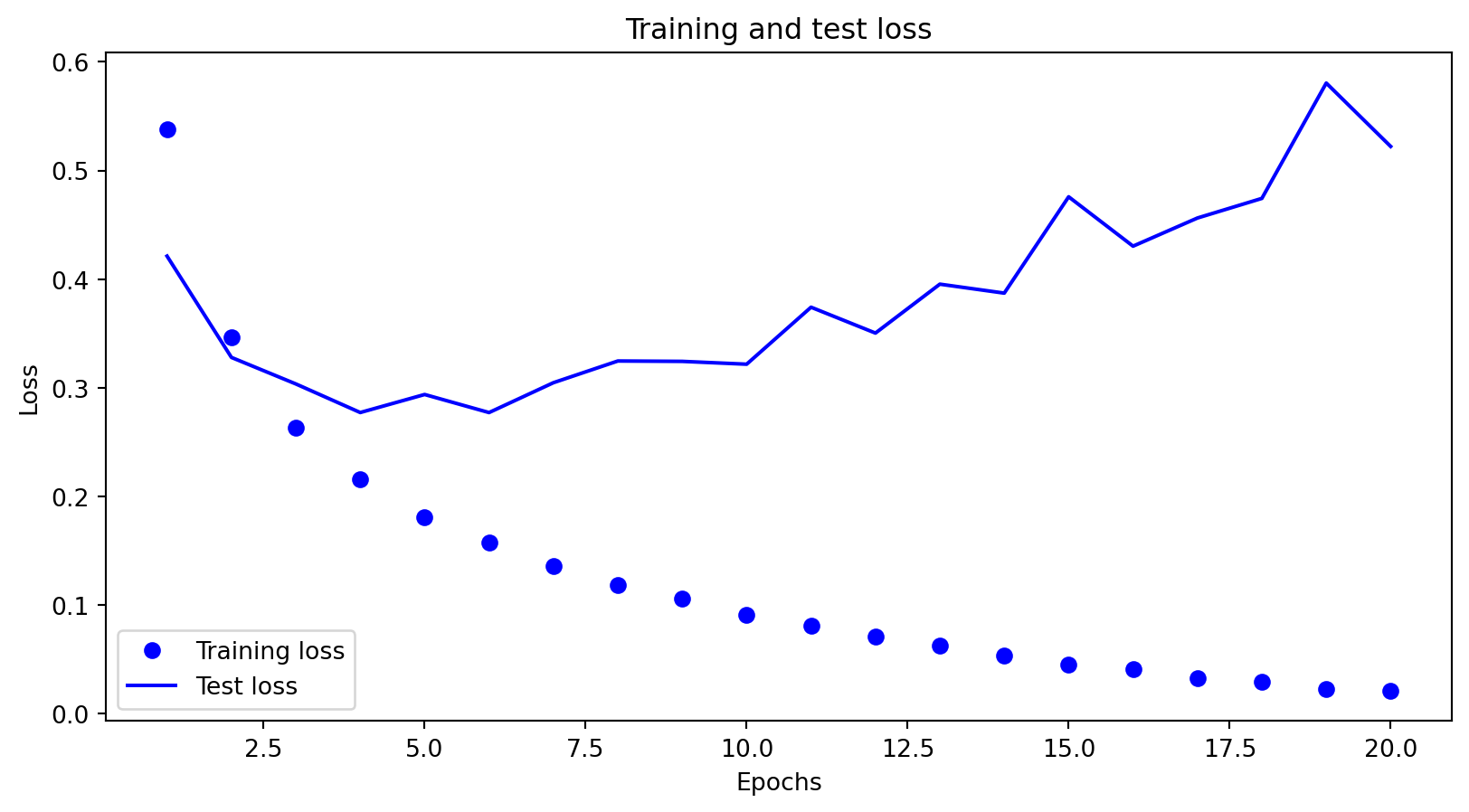
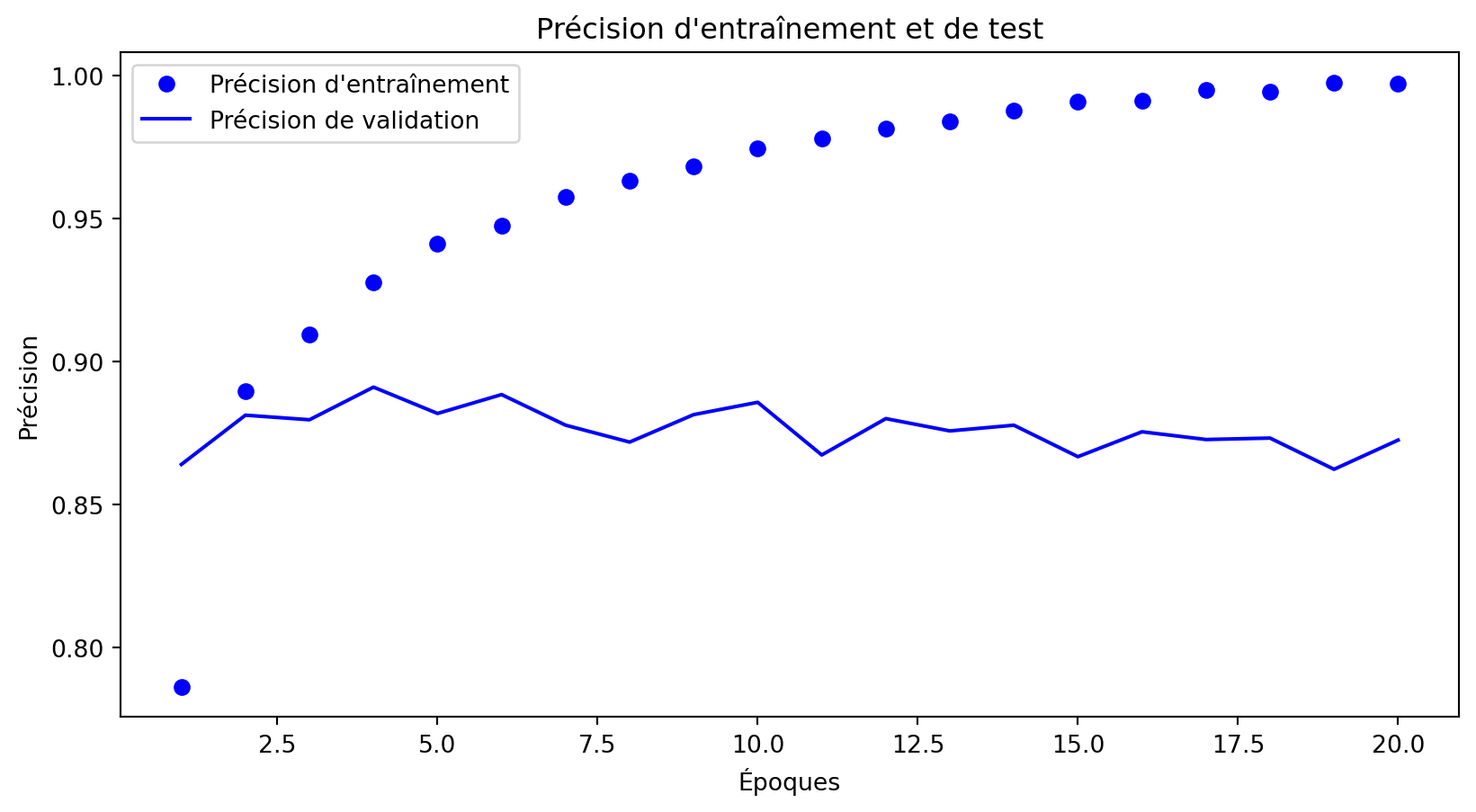
_ = plot_fold_predictions(1, X, y, X_grid, y_true_grid, n_splits=5)